As natural wellness continues to gain traction globally, certain botanicals are taking centre stage. One of these is Kratom, a tropical plant known for its stimulating and sedative effects. The primary active compound in Kratom is Mitragynine (MIT) – a naturally occurring alkaloid that's been the subject of increasing scientific interest and public debate. In this blog, we examine Mitragynine's chemical structure, origins, effects on the human body, potential uses, and associated risks.
What is Mitragynine?
Mitragynine is the dominant indole alkaloid found in the leaves of the Mitragyna speciosa tree – a species native to Southeast Asia, particularly Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Papua New Guinea. Kratom has been traditionally used for centuries in these regions for its analgesic, energy-boosting, and mood-enhancing properties. In its native regions, Kratom was historically used by farmers and labourers to combat fatigue, relieve pain, and stay focused during long hours of physical work.

Chemical Structure
Mitragynine's chemical structure is like a blueprint that shows how the molecule is built. Imagine it as a tiny, detailed puzzle made of atoms, with each piece playing a role in how it affects the body. It belongs to a group of natural compounds called alkaloids, which are known for having strong effects on the brain and body (like caffeine or morphine). Its structure is complex and unique, which is why it can interact with certain receptors in the brain, especially the ones that control pain, mood, and energy – similar to how opioids work, but in a more natural and potentially milder way. So when you see the squiggly diagram with rings and lines (the chemical structure), it's really just a scientist's map showing how Mitragynine connects with your body on a microscopic level.
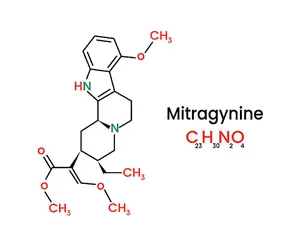
Mitragynine is chemically classified as a corynanthe-type monoterpenoid. The compound features:
- An indole nucleus (a structure common in many plant-based alkaloids)
- An ether bridge
- A methoxy group contributes to its psychoactive properties
Effects on the Human Body
Mitragynine acts primarily on opioid receptors, particularly the mu-opioid receptor, but also interacts with adrenergic and serotonergic systems. This unique interaction leads to a dual action depending on the dosage:
- Low doses (1-5g of dried leaf): Stimulant-like effects – enhanced energy, alertness, and sociability.
- Moderate to high doses (5-15g): opioid-like sedative and analgesic effects – relief from pain, relaxation, and sometimes euphoria.
Unlike traditional opioids, Mitragynine is a partial agonist, meaning it stimulates the receptor but with lower efficacy, potentially contributing to a reduced risk of respiratory depression (a primary cause of opioid overdose).
Traditional and Modern Uses
Historically, Kratom leaves were chewed or brewed into tea by manual labourers in Southeast Asia to combat fatigue, relieve pain, and boost productivity. On a cultural note, Kratom was so widely used in Thailand that it was banned in 1943 under colonial-era opium laws, not due to its harms, but because it interfered with the opium tax trade. Traditional applications laid the foundation for modern interest and applications.

Uses include:
- Natural Pain relief (especially chronic pain): Mitragynine interacts with mu-opioid receptors, producing analgesic (pain-relieving) effects similar to mild opioids, without the same level of respiratory suppression.
- Mood enhancement and anxiety reduction: At lower doses, it can act as a stimulant, promoting a sense of well-being, alertness, and mild euphoria.
- Aid in opioid withdrawal: Some users report using Kratom to ease withdrawal symptoms from prescription or illicit opioids. Mitragynine may help by binding to opioid receptors without triggering the intense high or crash of synthetic opioids.
- Anxiety and Stress Reduction: The calming properties of higher doses of Kratom are said to reduce stress and anxiety, offering a natural alternative to pharmaceutical anxiolytics.
- Relieving Fever and Gastrointestinal Issues: Local healers used Kratom infusions for fever reduction, diarrhoea, and intestinal cramps, often pairing it with other herbal remedies.
- Ritual and Social Use: In some regions, Kratom was consumed socially or ceremonially – shared among friends or used in small community gatherings, much like betel nut or kava.
- Increased focus and energy: Traditionally used to increase productivity, MIT may enhance mental clarity and motivation, especially in low to moderate doses.
In wellness communities, it is sometimes used as a natural alternative to pharmaceuticals for mood support and fatigue management. While many users report benefits, these uses are not currently approved by major regulatory bodies due to a lack of standardised clinical trials.
Adverse Effects and Controversy
While many users report positive experiences with Mitragynine, its use remains controversial due to potential adverse effects and regulatory concerns. Common side effects include nausea, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness and in higher doses, sedation or confusion. Long-term or excessive use may lead to dependence, with withdrawal symptoms resembling those of opioids, such as irritability, insomnia, and muscle aches. Although Kratom is often promoted as a natural alternative to pharmaceutical opioids, its interaction with opioid receptors has raised red flags among health authorities. Reports of liver toxicity, seizures, and, in rare cases, fatalities (often involving other substances) have led to calls for more regulation and research. As a result, Kratom is banned or restricted in several countries and is under review by global health agencies, including the FDA and WHO. Despite this, supporters argue that responsible, informed use can offer therapeutic value, especially when compared to more harmful synthetic drugs.
Legal and Regulatory Status
Kratom's legal status varies globally:
- Legal but regulated in South Africa, the U.S. (in most states), and Canada
- Banned in some countries, including Thailand (historically), Malaysia, and parts of Europe
- The FDA and DEA in the U.S. have issued warnings, but it remains unscheduled federally

The World Health Organisation (WHO) reviewed Kratom in 2021 and concluded that there was insufficient evidence to recommend a global ban, but emphasised the need for further research and regulation.
Conclusion: Natural Remedy or Risky Stimulant?
Mitragynine is a complex, powerful compound that offers both promise and peril. As interest in natural alternatives to pain relief and mental wellness grows, so does curiosity about Kratom and its key active alkaloid. While its traditional roots and anecdotal benefits are undeniable, responsible use, regulatory oversight, and scientific validation are essential.
We believe in informed choices rooted in science and transparency. If you are exploring Kratom as part of your wellness journey, we recommend researching thoroughly, sourcing from trusted suppliers, and consulting with healthcare professionals before use.
Sources:
- Kruegel, A.C., and Grundmann, O. (2018) The medicinal chemistry and neuropharmacology of kratom: A preliminary discussion of a promising medicinal plant and analysis of its potential for abuse. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 163.
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA): Kratom profile
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) - Title: FDA and Kratom - www.fda.gov/news-events/public-health-focus/fda-and-kratom.
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) - Title: Kratom Drug Facts - www.nida.nih.gov/publications/drugfacts/kratom.
Disclaimer: This blog supports responsible cannabis use.
The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as health or medical advice. Always consult a physician or other qualified health provider regarding any questions you may have about a medical condition or health objectives.